Root directory path is simply (/). Everything in file system is organized under this root directory. meaning: if I access say one Linux OS machine, then its default path is /
above dgm is not 100% accurate as I had 5yr old understanding but is not wrong either to del.
So, understanding more to how linux adds files - yes, its kind of fractal, look below:
Also, note: Permissions: Since /usr/local is typically a system-wide directory,
using sudo is necessary for creating files and directories there.
Be cautious with permissions to avoid affecting system files.
System-Wide Implications: Creating a virtual environment in /usr/local makes it accessible system-wide,
BUT THIS MIGHT NOT BE ideal if you're managing project-specific dependencies.
Consider creating virtual environments in home directory unless you have specific reason for using /usr/local.
I must not had paid attention to kernel. otherwise how clear its to me now.
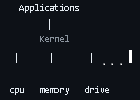
kernel is middle tier which connects to hw resources. kernel doesnt always have to be terminal or bash CLI stuffs. It can be os (thanks to Linus who must have painstakingly written all those lines which lets you control w mouse).
all those linux cmds like sudo, apt are recognized because Linus had written defined it as packages in C and assembly lang while writing Linux kernel. btw he didnt write it from scratch tho. he wrote on top of GNU framework, which was revolution against all proprietary locked Unix. very related my next article
Windows cant be said kernel but Linux is both kernel n os is both kernel and OS).
While Linux doesn’t have a central registry, tools and utilities are available for managing system configuration. These include:
a) Package Managers: Tools like apt, yum, dnf, etc., often handle configuration files as part of package installation and removal.
b) Configuration Management Systems: Tools like Ansible, Puppet, Chef, and SaltStack provide ways to automate configuration management across multiple systems, enforcing desired states defined in configuration files.
Windows: registry is centralized hierrachical database of windows os which stores config, settings etc configuration. jasto maile aaja taskbar vertical align gare vane tespachi kholda vertical nai vayera basira hunchh -ho yestai yestai vividh, yi sbae kura registry ma store hunchh.
HKLM= HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE, is a Windows Registry tree that contains configuration data that is used by all users in Windows. This includes information about Windows services, drivers, programs that automatically run for every user, and general OS settings.
Image Ka:
then, I wanted to install vscode as I had manually downloaded vscode from it official website instead of
sudo apt update
#1.Install dependencies
sudo apt install software-properties-common apt-transport-https wget
#2.Import Microsoft GPG key:
wget -q https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc -O- | sudo apt-key add -
#3.Enable vscode repository
sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://packages.microsoft.com/repos/vscode stable main"
#4.install vscode
sudo apt update
sudo apt install code
n so had missed 4th step.
I faced this-> issue while doing 4th step manually
sudo apt purge package_name_forEg_python3-pip removes package+ configFiles but remove just removes package
then after sudo apt autoremove removes any dependencies that were installed with the package but are no longer needed.